Spicy food has been a subject of fascination for many, not only for its delicious flavors but also for its potential effects on the brain. While the idea that spicy food can “stimulate” the brain may sound intriguing, it’s essential to clarify what this means and what science has to say about it. In this blog post, we’ll explore the relationship between spicy food and the brain.
Capsaicin – The Spicy Molecule:
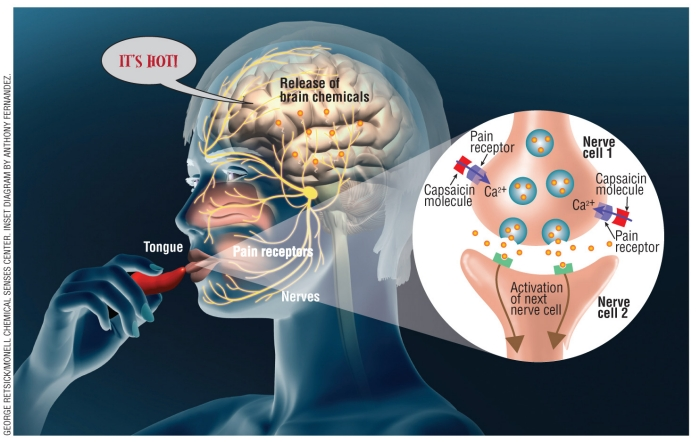
The primary component responsible for the spicy sensation in foods is capsaicin. It’s found in various chili peppers and creates a burning sensation when it interacts with receptors in your mouth and on your tongue. While this sensation can be intense and even uncomfortable, it does have some interesting effects on the brain.
Endorphin Release:

Capsaicin can trigger the release of endorphins in your brain. Endorphins are natural painkillers and mood elevators, often associated with the “feel-good” sensation. This is why some people enjoy the spicy “kick” and even find it addictive. It’s important to note that endorphin release can vary from person to person.
Increased Alertness:

Eating spicy food can lead to increased alertness and heightened senses. The spicy sensation can jolt your body and mind awake, which is why some people opt for spicy foods in the morning or when they need a pick-me-up.
Improved Cognitive Function:
Some studies suggest that capsaicin may have cognitive benefits. Research has shown that it may improve memory and potentially reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings conclusively.
Thermogenesis and Metabolism:
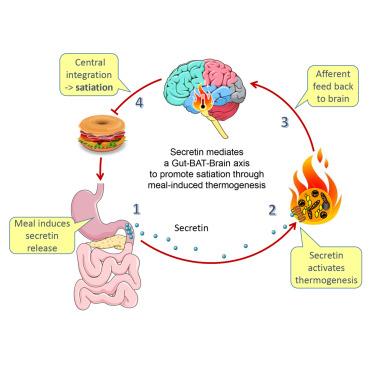
Spicy foods can increase thermogenesis, which is the process of generating heat in your body. This can lead to a temporary boost in metabolism. While this doesn’t directly stimulate the brain, it can provide a burst of energy that may help you feel more awake and alert.
Moderation is Key:

While some level of spiciness can have these potential brain-boosting effects, it’s important not to overindulge. Eating extremely spicy foods can lead to discomfort and even digestive issues. Moderation is key to enjoying the benefits of spiciness without any negative side effects.
Individual Variations:
People have different tolerances for spicy foods, and their reactions can vary widely. Some individuals may find spicy food invigorating, while others may experience discomfort or even pain.
In conclusion, while spicy food may not directly “stimulate” the brain in the way that caffeine or other stimulants do, it can have various effects on your body and mind. These effects include the release of endorphins, increased alertness, and potential cognitive benefits. Whether you enjoy spicy food for its flavor or its potential brain-boosting properties, it’s essential to listen to your body and consume it in moderation to fully enjoy the experience.